
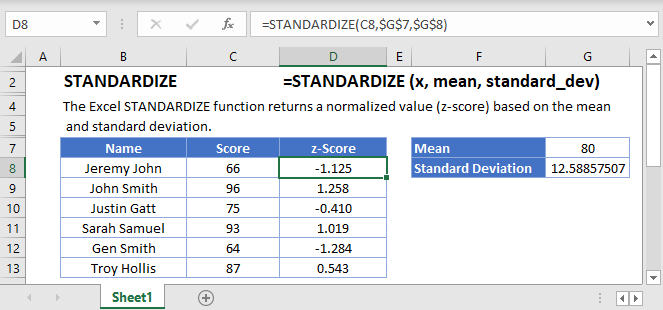
Then, to calculate the probability for a SMALLER z-score, which is the probability of observing a value less than x (the area under the curve to the LEFT of x), type the following into a blank cell: = NORMSDIST( and input the z-score you calculated). To make things easier, instead of writing the mean and SD values in the formula you could use the cell values corresponding to these values. Now to calculate the z-score type the following formula in an empty cell: = (x – mean) /. For example, if the range of scores in your sample begin at cell A1 and end at cell A20, the formula = STDEV.S (A1:A20) returns the standard deviation of those numbers. Next, you mush calculate the standard deviation of the sample by using the STDEV.S formula. To calculate the z-score of a specific value, x, first you must calculate the mean of the sample by using the AVERAGE formula.įor example, if the range of scores in your sample begin at cell A1 and end at cell A20, the formula =AVERAGE(A1:A20) returns the average of those numbers. If there is less than a 5% chance of a raw score being selected randomly, then this is a statistically significant result. The probability of randomly selecting a score between -1.96 and +1.96 standard deviations from the mean is 95% (see Fig. Proportion of a standard normal distribution (SND) in percentages. For example, there is a 68% probability of randomly selecting a score between -1 and +1 standard deviations from the mean (see Fig.
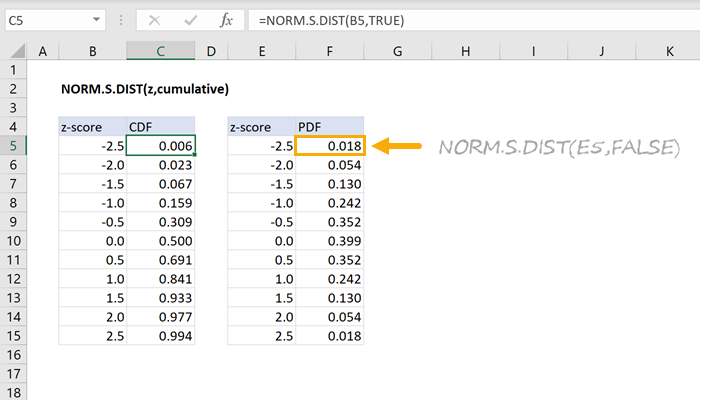
The SND allows researchers to calculate the probability of randomly obtaining a score from the distribution (i.e. Therefore, one standard deviation of the raw score (whatever raw value this is) converts into 1 z-score unit. The standard deviation of any SND always = 1.For example, if the distribution of raw scores if normally distributed, so is the distribution of z-scores. z-distribution) is always the same shape as the raw score distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
